Climate Change Leads to 41 Extra Days of Dangerous Heat in 2024
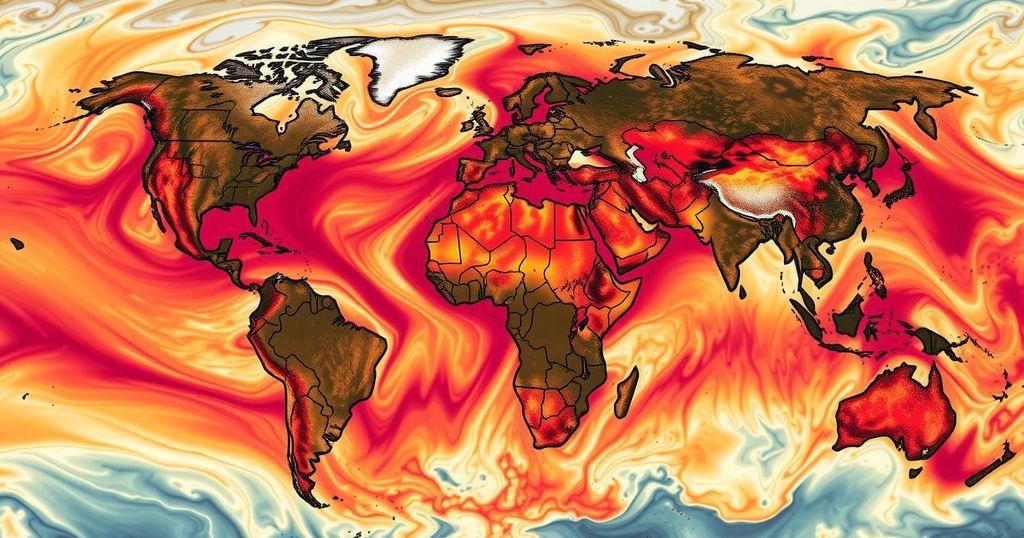
In 2024, the globe faced 41 extra days of dangerous heat due to climate change, with various regions experiencing severe weather conditions. Researchers linked many extreme weather events to climate change, emphasizing the urgent need for climate action as the world potentially approaches critical warming thresholds.
In 2024, the world experienced an average of 41 additional days of dangerous heat attributed to human-induced climate change, as reported by climate researchers. The findings indicate a significant escalation in extreme weather patterns, linking climate change to the intensity and frequency of adverse weather events such as heatwaves, droughts, and tropical storms. This year was characterized by record-breaking temperatures and environmental crises that severely affected numerous communities across the globe, from the scorching climates in California and Greece to the extreme conditions in West Africa and Southeast Asia.
The research conducted by World Weather Attribution and Climate Central emphasizes that the extreme heat resulted in millions enduring harrowing conditions, with some regions facing over 150 days of extreme temperatures. With the planet approaching the Paris Agreement’s crucial warming threshold, the urgency for immediate action against climate change is accentuated. Moreover, the overwhelming evidence suggests that the impacts of climate change are disproportionately felt by the most vulnerable populations, particularly in less developed countries.
The ongoing climate crisis has reached alarming levels, characterized by unprecedented heat and severe weather events globally. As scientific analyses reveal the profound effects of climate change on weather patterns, the linkage between rising temperatures and increased frequency of deadly heat waves becomes evident. The year 2024 serves as a critical indicator of the potential futures faced by communities if actionable measures against climate change are not adopted. Researchers are utilizing advanced methods to study daily temperatures in relation to historical data, demonstrating the direct repercussions of human activities on global warming and weather phenomena.
The findings regarding the increase in dangerous heat days serve as a stark reminder of the critical state of climate change today. With strong evidence linking heat events to human activities, the necessity for immediate global action to mitigate climate-related disasters has never been more pressing. As the impacts of climate change are felt worldwide, efforts must be coordinated across nations to enhance preparedness and foster resilience in the face of rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
Original Source: apnews.com






